Where to Find Spreadsheets for Lime Soda Water Softening Calculations
For Excel spreadsheets to make lime soda water softening calculations, click here to visit our spreadsheet store. Obtain convenient, easy to use spreadsheets for lime soda water softening calculations at reasonable prices. Read on for information about the use of Excel spreadsheets for this application.
Water Hardness Background for Lime Soda Water Softening
Hardness in water is caused by divalent cations, primarily Ca++ and Mg++. Water hardness is sometimes classified in terms of the cation as calcium hardness or magnesium hardness. The sum of the two is typically referred to as total hardness or simply hardness. For lime soda water softening chemistry it is also necessary to have knowledge about the anions in the water. Hardness due to Ca++ or Mg++ together with carbonate (CO3=) or bicarbonate (HCO3–) is called carbonate hardness. At typical drinking water pH, the anion for carbonate hardness is almost completely bicarbonate. Hardness due to Ca++ or Mg++ together with any anion other than carbonate/bicarbonate is called noncarbonate hardness.
The two most widely used methods for softening water (reducing hardness to an acceptable level) are lime soda water softening and ion exchange softening. Ion exchange softening is typically used for groundwater softening and for home water softeners, while lime soda water softening is the usual method of choice for a surface water source. This article is about lime soda water softening.
Lime Soda Water Softening Background
Lime soda softening uses addition of lime and soda ash to remove Ca++ and Mg++ ions, bringing their concentration down to an acceptable level. The lime may be in the form of quicklime (CaO) or hydrated lime (Ca(OH)2), also called slaked lime. Soda Ash is Na2CO3. Calcium ions are removed be bringing the pH level up enough to convert Ca(HCO3)2 to CaCO3, which is relatively insoluble in water and precipitates out down to a residual level of about 30 to 40 mg/L. Magnesium is precipitated out as Mg(OH)2. Some lime soda softening processes require addition of carbon dioxide (recarbonation) at one or more points in the process to reduce the pH.
Lime Soda Water Softening Process Alternatives
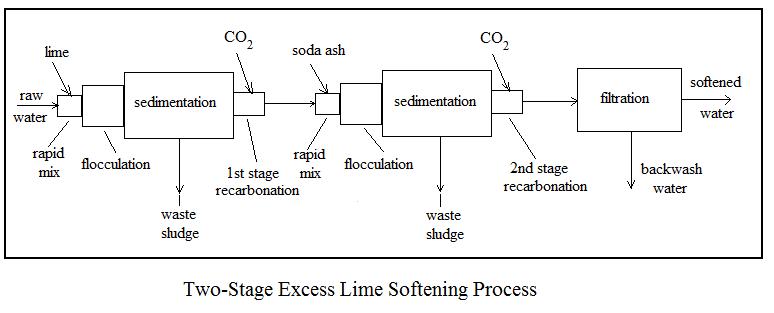
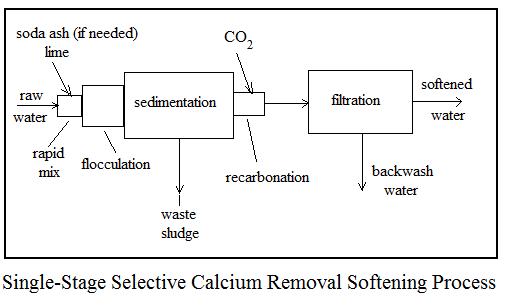
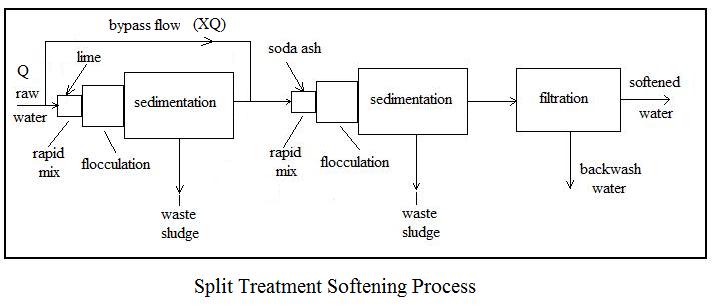
Three common alternative processes for lime soda water softening are i) two-stage, excess lime treatment, ii) single-stage, selective calcium removal, and iii) split treatment. Flow diagrams and a brief description of each follows.
The two-stage, excess lime softening process provides the most complete softening. It is capable of removing calcium and magnesium carbonate and noncarbonate hardness, down to the solubility limits of about 30 to 40 mg/L of calcium hardness and about 10 mg/L of magnesium hardness.
The single-stage, selective calcium removal process is suitable for water sources with 40 mg/L or less of magnesium hardness. As indicated by its name, this process removes only calcium hardness and has no effect on magnesium hardness. A suitably softened water should have less than 40 mg/L of magnesium hardness, so this is the limiting factor for use of this simpler process, which requires less chemicals.
The split treatment softening process illustrated in the diagram above is another alternative for water sources with more than 40 mg/L of magnesium hardness. It is a two –stage process, but typically requires less chemicals than the excess lime process, and typically doesn’t require recarbonation.
Spreadsheets for Lime Soda Water Softening Calculations
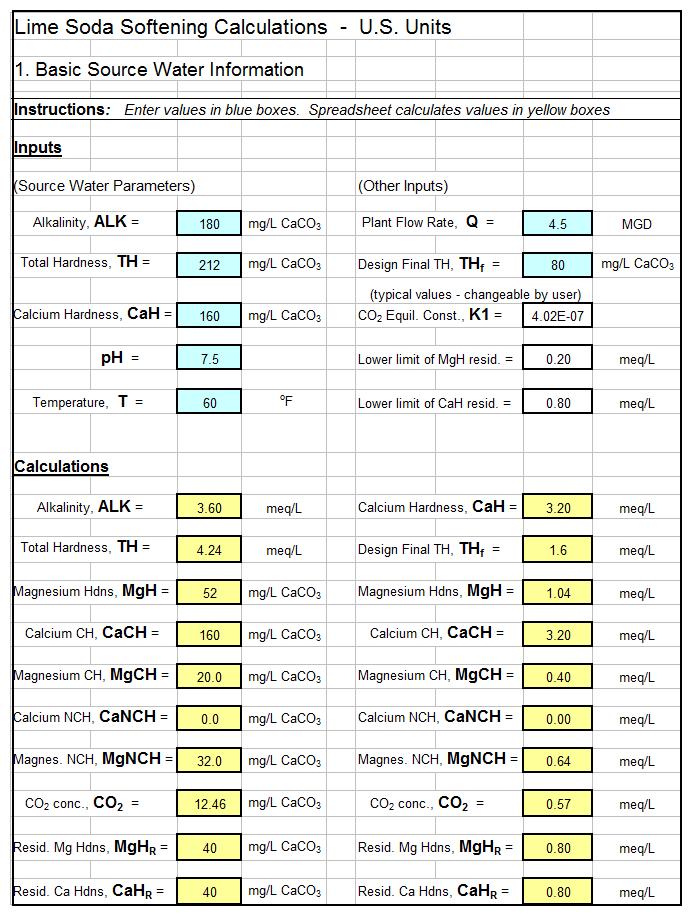
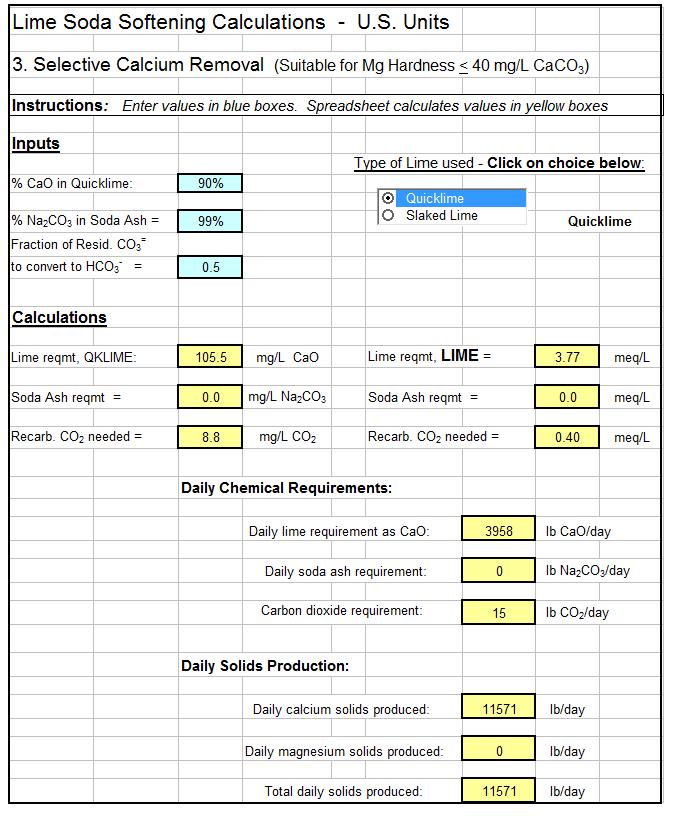
There are logical choices (e.g. Is Alkalinity > Hardness or is Hardness > Alkalinity) in calculating the types of hardness in a water supply source. Also there are logical choices and numerous equations used in calculating chemical dosages for lime soda water softening. This makes a spreadsheet a very good vehicle for making lime soda water softening calculations. The first spreadsheet screenshot below shows the type of spreadsheet calculations that can be made for identifying the types of hardness in a source water. The second screenshot shows dosage calculations for a selective calcium removal softening process. For low cost, easy to use spreadsheets to make these calculations as well as similar calculations for the excess lime and split treatment lime soda processes, in S.I. or U.S. units, click here to visit our spreadsheet store.
References
1. Viessman, Warren., Jr & Hammer, Mark J., Water Supply and Pollution Control, 6th Ed., Addison Wesley, Menlo Park, CA, 1998
2. Bengtson, Harlan H., “Lime Soda Softening Process Calculations,” an Amazon Kindle ebook.
3. Bengtson, Harlan H., “Lime Soda Water Softening Calculations,” an online, self-study, continuing education PDH course for Professional Engineers.