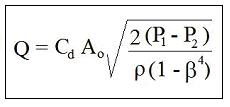Where to Find a Gas Compressibility Factor Calculator Excel Spreadsheet
To obtain a gas compressibility factor calculator Excel spreadsheet, click here to visit our spreadsheet store. Look in the Fluid Properties category on the Download page. This Excel spreadsheet is intended for calculation of the compressibility factor of a gas using the Redlich-Kwong equation of state. You can buy a convenient gas compressibility factor calculator Excel spreadsheet for a very reasonable price. This spreadsheet calculates the compressibility factor of a gas from the gas temperature, gas pressure, and the critical pressure and critical temperature of the gas. It is available in either U.S. or S.I. units. Read on for information about using a gas compressibility factor calculator Excel spreadsheet.
Background for Gas Compressibility Factor Calculator Excel Spreadsheet
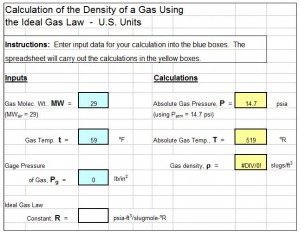
The compressibility factor of a gas is used in several types of calculations including calculation of real gas density. The Ideal Gas Law, PV = nRT, can be used to calculate the density of a gas that exhibits ideal gas behavior by introducing the molecular weight of the gas and solving for gas density to give: ρ = MW*P/R*T.
For information on the use of the ideal gas to calculate gas density, see the article, “Air Density Calculator Excel Spreadsheet.”
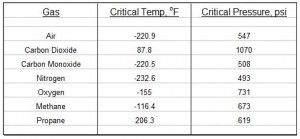
Conditions required for ideal gas behavior are pressure << critical pressure and/or temperature >> critical temperature. For gases that don’t exhibit ideal gas behavior, the compressibility factor, Z can be introduced to give: ρ = Z*MW*P/R*T.
The Redlich-Kwong Equation of State
One possibility for a gas compressibility factor calculator Excel spreadsheet is through the use of the Redlich-Kwong equation of state, which is shown below:
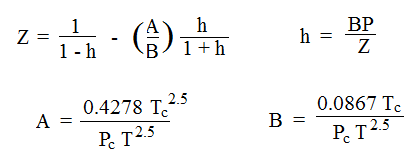 A, B, and h are constants calculated as shown. The compressibility factor, Z, can be calculated for known values of the gas temperature, T, the gas temperature, P, and the critical temperature and pressure of the gas. The temperatures should be in K and the pressures in atm for use of the equations given above. Calculation of Z requires an iterative calculation because the equations can’t be solved explicitly for Z.
A, B, and h are constants calculated as shown. The compressibility factor, Z, can be calculated for known values of the gas temperature, T, the gas temperature, P, and the critical temperature and pressure of the gas. The temperatures should be in K and the pressures in atm for use of the equations given above. Calculation of Z requires an iterative calculation because the equations can’t be solved explicitly for Z.
Example Gas Compressibility Factor Calculator Excel Spreadsheet
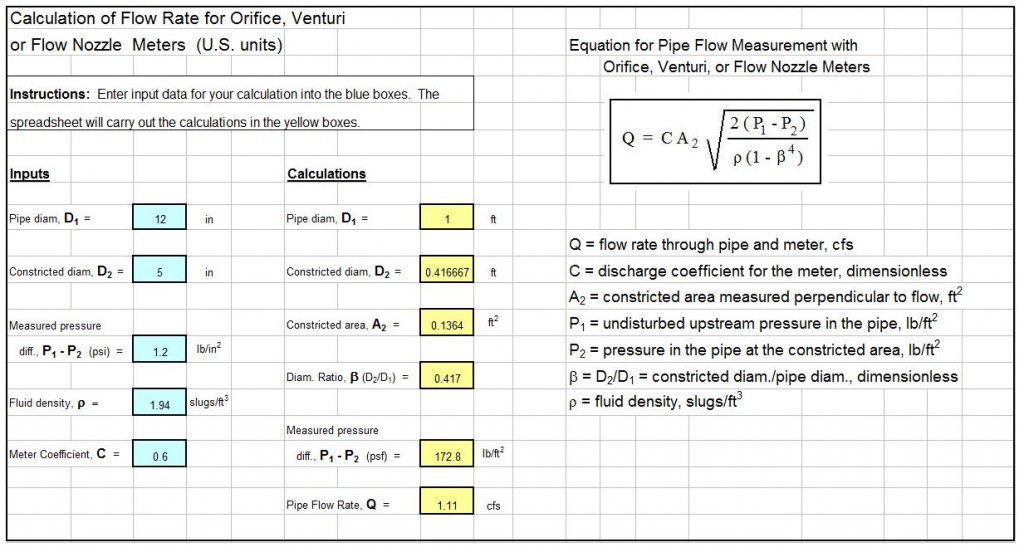
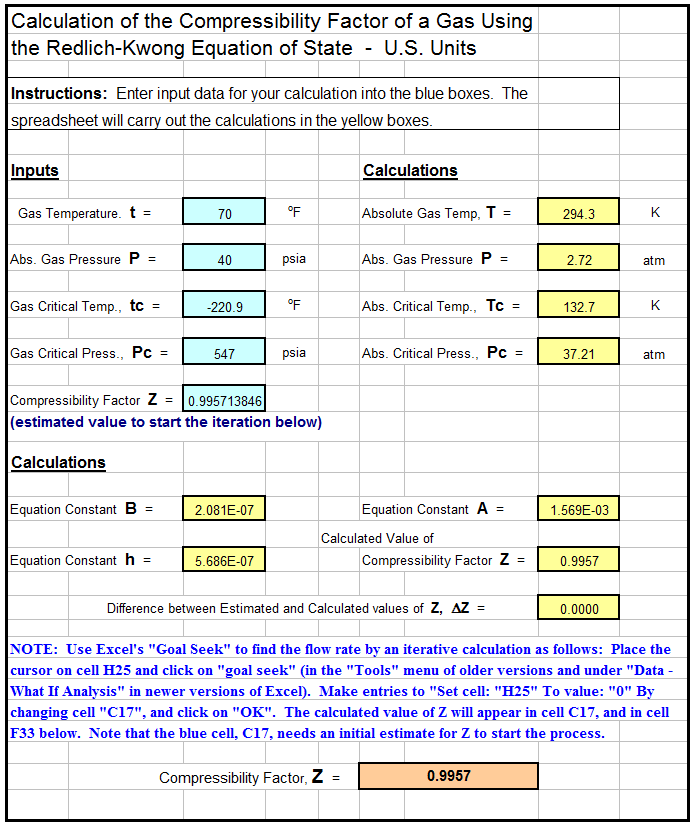
An example gas compressibility factor calculator Excel spreadsheet is partially shown in the image below. This Excel spreadsheet can be used to calculate the compressibility factor of a gas, based on user input values for gas temperature, gas pressure, and the critical temperature and pressure of the gas. This Excel spreadsheet, as well as others for fluid property calculations, is available in either U.S. or S.I. units for a very reasonable price in our spreadsheet store.
 References
References
1. Otto Redlich, and J.N.S. Kwong, “On the Thermodynamics of Solutions. V. An Equation of State. Fugacities of Gaseous Solutions”, Chemical Reviews 44 pp. 233-244 (1949).
2. Bengtson, Harlan H., Redlich Kwong Compressibility Factor Spreadsheet, an informational online blog article.