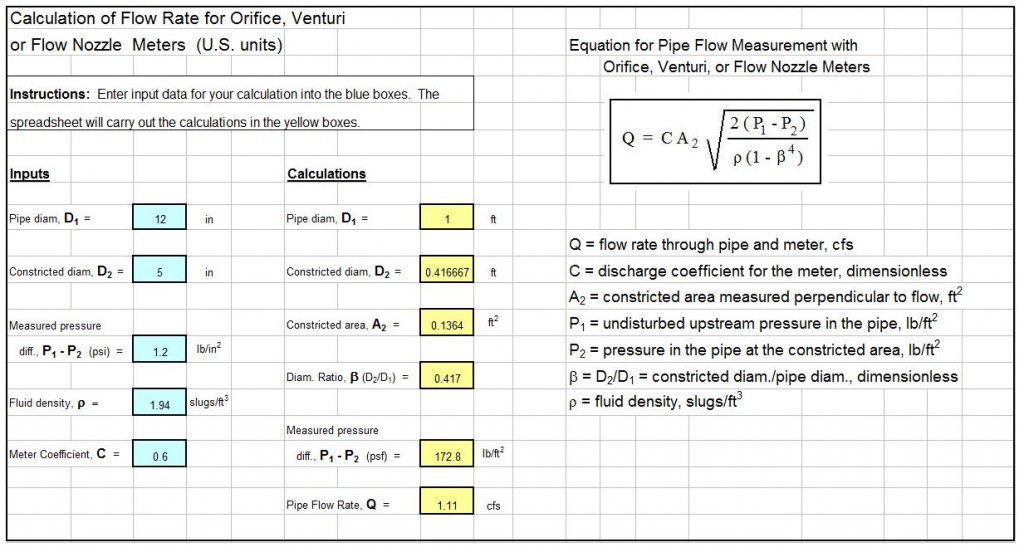
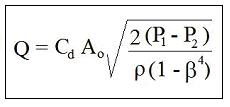Where to Find Spreadsheets for ISO 5167 Orifice Plate Flow Meter Calculations
For Excel spreadsheets to make ISO 5167 orifice plate flow meter calculations, click here to visit our spreadsheet store. Why use online calculators or try to use the incredibly long ISO 5167 equations for hand calculations when you can buy a spreadsheet for gas flow or liquid flow, large bore or small bore ISO 5167 orifice plate flow meter calculations for only $15.95 each. Read on for information about the use of an Excel spreadsheet for large bore and small bore orifice meter/gas flow rate or liquid flow rate calculations.
Orifice Meter Background for ISO 5167 Orifice Plate Flow Meter Calculations
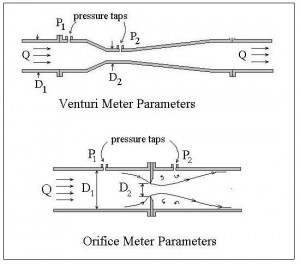
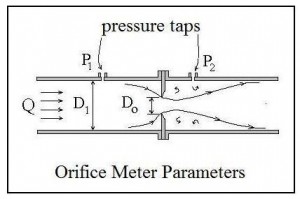 For background on orifice meters and the orifice meter coefficient, see the articles, “Excel Spreadsheets for Orifice and Venturi Flow Meter Calculations” and “Calculate an Orifice Coefficient with ISO 5167.” The diagram at the left shows the general orifice meter configuration and some of the parameters used in calculations. Equations from ISO 5167-2:2003 are presented in the next section.
For background on orifice meters and the orifice meter coefficient, see the articles, “Excel Spreadsheets for Orifice and Venturi Flow Meter Calculations” and “Calculate an Orifice Coefficient with ISO 5167.” The diagram at the left shows the general orifice meter configuration and some of the parameters used in calculations. Equations from ISO 5167-2:2003 are presented in the next section.
Equations for ISO 5167 Orifice Plate Flow Meter Large Bore Calculations
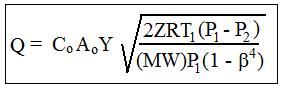 The equations for pipes with diameter between 2 in. and 40 in (50 mm to 1000 mm) are given in Reference #1 at the end of this article, ISO 5167-2:2003. The equations are summarized here. The commonly used equation for compressible fluid (gas) flow rate is shown at the right, where the parameters are defined as follows:
The equations for pipes with diameter between 2 in. and 40 in (50 mm to 1000 mm) are given in Reference #1 at the end of this article, ISO 5167-2:2003. The equations are summarized here. The commonly used equation for compressible fluid (gas) flow rate is shown at the right, where the parameters are defined as follows:
- Q = flow rate through pipe and meter, cfs (m3/s for S.I. units)
- Co = orifice discharge coefficient, dimensionless
- Ao = orifice area, ft2 (m2 for S.I. units)
- P1 = upstream absolute pressure in the pipe, lb/ft2 (kN/m2 for S.I. units)
- P2 = pressure at the downstream pressure tap, lb/ft2 (kN/m2 for S.I. units)
- β = Do/D1 = orifice diam./pipe diam., dimensionless
- Z = compressibility factor of the gas at P1, T1
- R = Ideal Gas Law Constant = 345.23 psia-ft3/slugmole-oR ( or 8.3145 kN-m/kgmole-oK for S.I. units)
- MW = molecular weight of the gas
- T1 = upstream absolute temperature in the pipe, oR (oK for S.I. units)
- Y = Expansion Factor – see equation for Y below
Y = 1 – (0.351 + 0.265 β4 + 0.93 β8)[ 1 – (P2/P1)1/k ]
where: k is the Specific Heat Ratio (Cp/Cv) of the flowing gas
The orifice coefficient, Co, can be calculated from the following equations:
 Where Re is the Reynolds number in the pipe ( Re = DVρ/μ )
Where Re is the Reynolds number in the pipe ( Re = DVρ/μ )
An Excel Spreadsheet as an Orifice Meter/Gas Flow Calculator
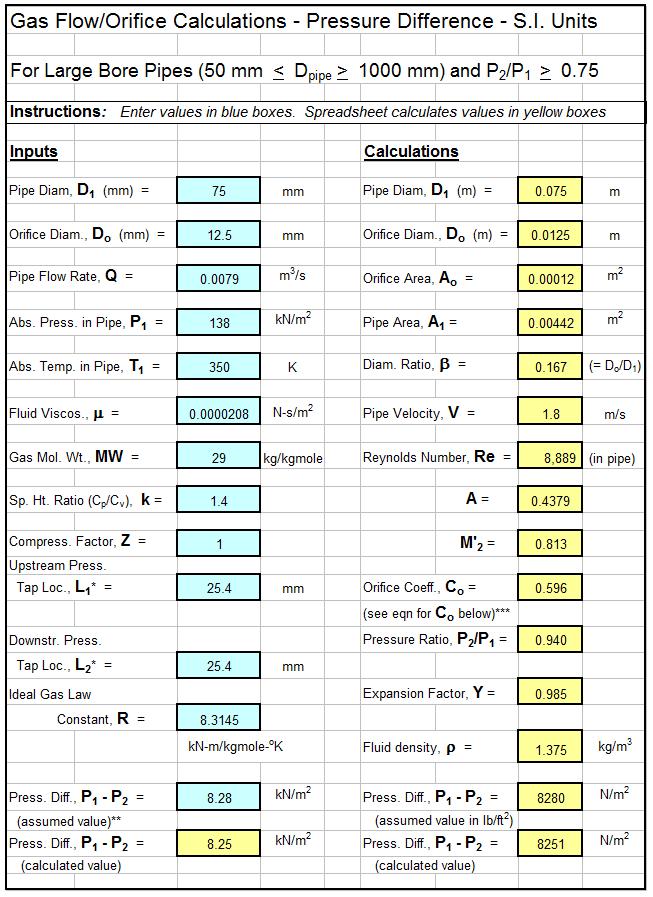
The Excel spreadsheet template shown below can be used to calculate gas flow rate, required orifice diameter, or pressure difference across the orifice, if the other two are known. This spreadsheet is for large bore pipes (2 in. to 40 in diameter) and uses S.I. units. The image shows just the first page of the worksheet to calculate gas flow rate. Why bother to make these calculations by hand? This Excel spreadsheet and others with similar calculations for ISO 5167 orifice plate flow meter calculations are available in either U.S. or S.I. units at a very low cost (only $14.95 each) in our spreadsheet store. There are also spreadsheets for large bore orifice meter calculations for liquid flow and for small bore orifice meter calculations (gas flow or liquid flow). The small bore spreadsheets are for pipes with diameter between 1/2 inch and 1 1/2 inches (12 mm to 40 mm), and use slightly different equations from ASME MFC-14M:2001.
References:
1. U.S. Dept. of the Interior, Bureau of Reclamation, 2001 revised, 1997 third edition, Water Measurement Manual.
2. International Organization of Standards – Measurement of fluid flow by means of pressure differential devices inserted in circular cross-section conduits running full. Reference number: ISO 5167-2:2003.
4. Bengtson, Harlan H., “Orifice or Venturi Pipe Flow Meters: for Liquid Flow or Gas Flow,” an Amazon Kindle ebook.
5. Bengtson, Harlan H., “Flow Measurement in Pipes and Ducts,” an online, self-study, continuing education course for Professional Engineers at www.CEDengineering.com.
6. Bengtson, Harlan H., “Orifice and Venturi Meters Pipe Flow Meters – for Liquid and Gas Flow,” an online, self-study, continuing education course for Professional Engineers at www.suncam.com.
7. Bengtson, Harlan H. “Orifice Gas Flow Calculation Excel Spreadsheets,” an online blog article.